What Is A Cell?
A cell is a single unit device which converts chemical energy to electrical energy.
What Is A Battery?
A battery is a container consisting of one or more cells, in which chemical energy is converted to electricity and is used as a source of power and can be charged.
The Lithium Ion Battery
A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery that uses lithium ions to transfer charge between the positive and negative electrodes during discharge and charging. It is commonly used in consumer electronics and has high energy density, good energy-to-weight ratio, and low self-discharge rate. IPhone uses built-in, high-quality lithium-ion batteries.
A schematic diagram of the same is shown below:
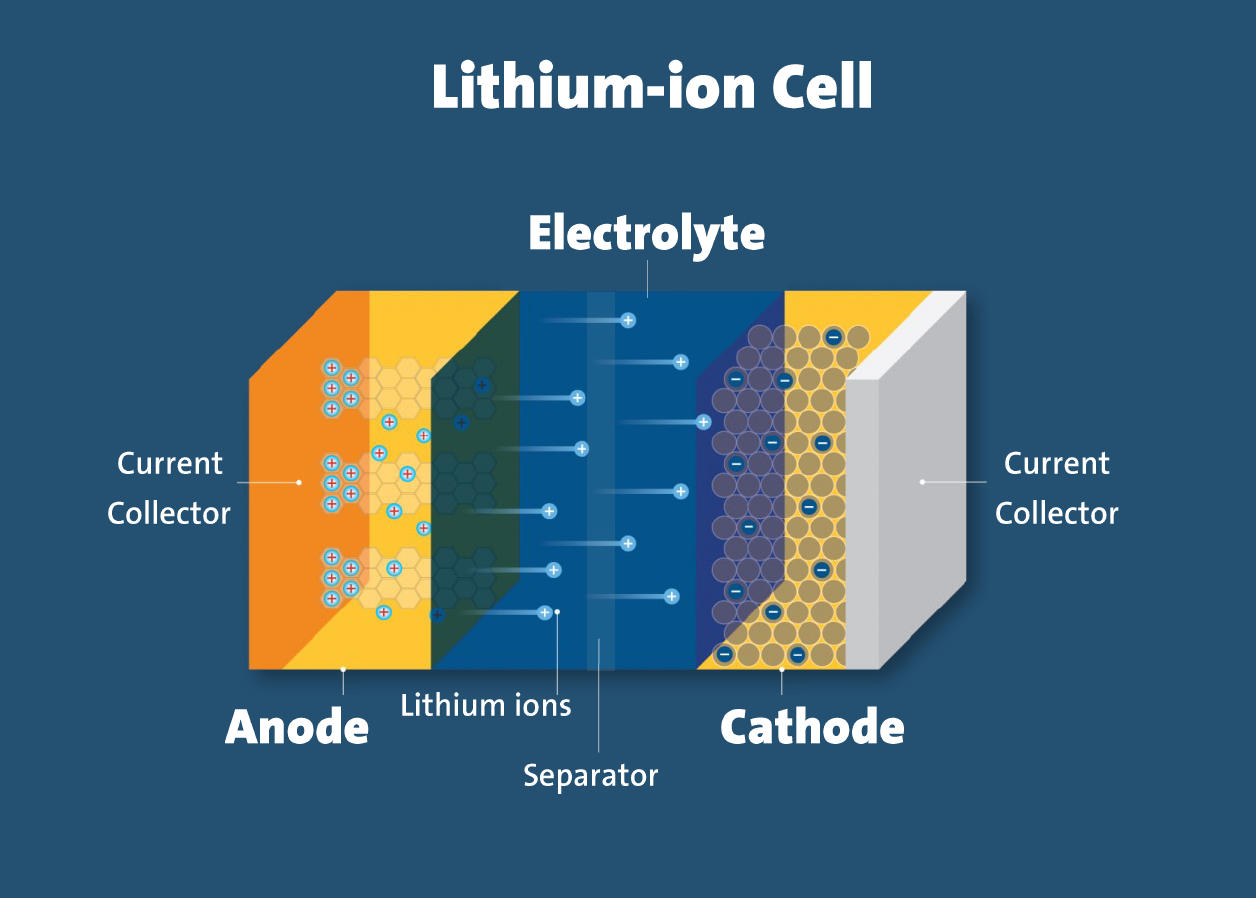
Explanation Of The Schematic Above Diagram Mentioned Below:
- Electrodes: The positively and negatively charged ends of a cell. Attached to the current collectors
- Anode: The negative electrode
- Cathode: The positive electrode
- Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that conducts electricity
- Current collectors: Conductive foils at each electrode of the battery that are connected to the terminals of the cell. The cell terminals transmit the electric current between the battery, the device and the energy source that powers the battery
- Separator: A porous polymeric film that separates the electrodes while enabling the exchange of lithium ions from one side to the other
How Does A Lithium-Ion Cell Work?
In a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions (Li+) move between the cathode and anode internally. Electrons move in the opposite direction in the external circuit. This migration is the reason the battery powers the device—because it creates the electrical current.
While the battery is discharging, the anode releases lithium ions to the cathode, generating a flow of electrons that helps to power the relevant device.
When the battery is charging, the opposite occurs: lithium ions are released by the cathode and received by the anode.
What Is A Lithium-Ion Battery Used For?
Lithium-Ion batteries are rechargeable and are used in many personal electronics such as cell phones, tablets, and laptops, E-Bikes, electric toothbrushes, tools, hover boards, scooters, and for solar power backup storage.
Is Lithium-Ion Battery The Best Battery?
They’re built to withstand many charge cycles with minimal loss in performance. Li-ion for High Energy Needs: For devices that need a lot of power but where space is limited, Li-ion batteries are the top choice due to their higher energy density.
What Is The Biggest Problem With Lithium Batteries?
The major issue with lithium-ion batteries overheating is a phenomenon known as thermal runaway. In this process, the excessive heat promotes the chemical reaction that makes the battery work, thus creating even more heat and ever more chemical reactions in a disastrous spiral.
Do Lithium Batteries Need A Special Charger?
One can use a normal Lead Acid Battery (without the de-sulfate mode) to charge a lithium battery. But, we recommend to use Battery Charger suitable for their chemistry. We also recommend checking all lithium batteries for low voltage every 3-4 months and charging as needed.
What Is A Lithium-Ion Battery Charger?
The Li-ion charger is a voltage-limiting device that has similarities to the lead acid system. The differences with Li-ion lie in a higher voltage per cell, tighter voltage tolerances and the absence of trickle or float charge at full charge.
[The lead-acid battery is a type of rechargeable battery first invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. It is the first type of rechargeable battery ever created. Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead-acid batteries have relatively low energy density.]
[Float charging is the technology and method of maintaining a battery in the charged condition by applying a continuous voltage and current at the minimum level]
What Is The Optimal Charging Temperature Charging For Lithium Battery?
Charging lithium batteries outside their recommended temperature range can lead to reduced capacity, internal damage, and potential failure. For optimal charging and extended battery life, it is recommended to: Charge lithium batteries between 0°C and 45°C (32°F to 110°F)
Charging Voltages For Lithium Batteries
Understanding the charging voltages for lithium batteries is crucial for maintaining battery health and performance. This includes knowing the appropriate voltages for the bulk, absorption, and float stages of charging.
For lithium batteries, the recommended voltage range for battery charging is between 14.2 and 14.6 volts. This may seem confusing because you may be wondering how a 12V battery is charged to 14.2 to 14.6 volts.
However, this voltage is achieved only during the charging process and it will taper off and drop back down to 13.6V for a fully charged 12V battery.
By adhering to the charging voltages specific to your lithium battery type, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Do I Need A Special Charger For Lithium Batteries?
Yes, you need a special charger for lithium batteries that can be set to the correct voltage and doesn’t have an automatic equalization mode enabled.
Is It OK To Leave A Lithium-Ion Battery On The Charger Overnight?
It is generally safe to leave a lithium-ion battery on the charger overnight, as they are designed to be left plugged in. However, power banks may overheat if not stored in a cool, dry place while charging. Thus, it is best to unplug and store in a safe location when not in use.
Now a days Li-ion or Li-ferro phosphate battery pack comes with BMS (Battery Management System), which protects the battery from over-charging or as well as deep discharging.
However, we at ESI design the profile of each battery charger suitable for its application.


